supraspinatus tear tests|incomplete full thickness tear supraspinatus : traders Diagnosis can be suspected clinically with provocative tests of the supraspinatous, infraspinatous, teres minor and subscapularis, but confirmation requires an MRI of the shoulder. Treatment can be nonoperative or operative depending on the chronicity of symptoms, severity of the tear, degree of muscle fatty atrophy, patient age and patient .
The MLS Laboratory Autoclaves are steam sterilisers in all sizes. Known for their safety and high control levels.
{plog:ftitle_list}
The autoclave needs to be able to consistently produce high-quality products out of a workpiece that is the world’s largest class in terms of both inner diameter and length.ASC Process Systems has announced the completion of the world's largest autoclave, which was fabricated on-site at the new Vought Aircraft facility in Charleston, SC. .

supraspinatus tear test pdf
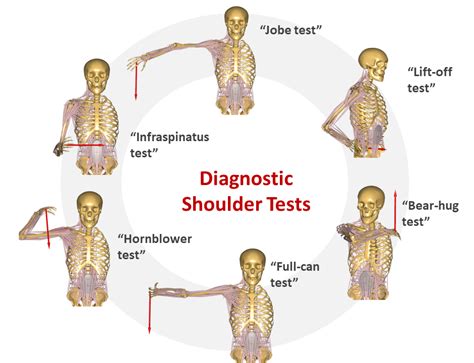
Supraspinatus Test. The supraspinatus tendon is the most frequently injured tendon of the rotator cuff. To test for integrity of the supraspinatus we can ask the patient to abduct both arms to 90° and then to bring them anteriorly with a 30° .Supraspinatus tears are normally present as partial or full-thickness tears. It can be asymptomatic or symptomatic. Partial thickness: Incomplete disruption of muscle fibres; Can progress to complete tear - Increasing pain is normally the first sign of the progression of a tear; Full thickness: Complete disruption of muscle fibresSupraspinatus Test. The supraspinatus tendon is the most frequently injured tendon of the rotator cuff. To test for integrity of the supraspinatus we can ask the patient to abduct both arms to 90° and then to bring them anteriorly with a 30° forward flexion. From this position, we will ask the patient to push both arms upwards against our .Special testing is generally performed following a full examination of the shoulder that includes but is not limited to patient history, mechanism of injury, clinical observation, bony and soft tissue palpation, assessment of active and passive physiological movements, assessment of passive arthokinematic / accessory joint mobility, neurological.
This test targets one of the rotator cuff muscles that most commonly tears at the tendon: the supraspinatus. To perform the empty can test, fully extend your bad arm and raise it to shoulder height, slightly outward from your body. Turn your hand downward, as if you are emptying a can or glass. Diagnosis can be suspected clinically with provocative tests of the supraspinatous, infraspinatous, teres minor and subscapularis, but confirmation requires an MRI of the shoulder. Treatment can be nonoperative or operative depending on the chronicity of symptoms, severity of the tear, degree of muscle fatty atrophy, patient age and patient .The drop arm test is used to assess for full thickness rotator cuff tears, particularly of the supraspinatus [1]. This can be useful when diagnosing sub-acromial pain syndrome (shoulder impingment) or to differentiate between shoulder and rotator cuff pathologies.
Rotator cuff tears are common injuries caused by damage to the muscles or tendons that stabilize your shoulder joint. They can be diagnosed by using a number of physical tests and imaging. Symptoms of a supraspinatus tear include: Sharp pain in the shoulder at the time of injury. Pain when the arm is rotated outwards and upwards. Increased pain and weakness when the arm is raised sideways between a 60-degree arc. Read more on how to .The Drop Arm Sign or Drop Arm Test is a common orthopedic test to assess for full-thickness tears of the supraspinatus and infraspinatus.This page describes the Drop Arm Test, a common test for a supraspinatus tear and/or rotator cuff tear. A video demonstration is included.
Supraspinatus tears are normally present as partial or full-thickness tears. It can be asymptomatic or symptomatic. Partial thickness: Incomplete disruption of muscle fibres; Can progress to complete tear - Increasing pain is normally the first sign of the progression of a tear; Full thickness: Complete disruption of muscle fibresSupraspinatus Test. The supraspinatus tendon is the most frequently injured tendon of the rotator cuff. To test for integrity of the supraspinatus we can ask the patient to abduct both arms to 90° and then to bring them anteriorly with a 30° forward flexion. From this position, we will ask the patient to push both arms upwards against our .Special testing is generally performed following a full examination of the shoulder that includes but is not limited to patient history, mechanism of injury, clinical observation, bony and soft tissue palpation, assessment of active and passive physiological movements, assessment of passive arthokinematic / accessory joint mobility, neurological.
This test targets one of the rotator cuff muscles that most commonly tears at the tendon: the supraspinatus. To perform the empty can test, fully extend your bad arm and raise it to shoulder height, slightly outward from your body. Turn your hand downward, as if you are emptying a can or glass. Diagnosis can be suspected clinically with provocative tests of the supraspinatous, infraspinatous, teres minor and subscapularis, but confirmation requires an MRI of the shoulder. Treatment can be nonoperative or operative depending on the chronicity of symptoms, severity of the tear, degree of muscle fatty atrophy, patient age and patient .
The drop arm test is used to assess for full thickness rotator cuff tears, particularly of the supraspinatus [1]. This can be useful when diagnosing sub-acromial pain syndrome (shoulder impingment) or to differentiate between shoulder and rotator cuff pathologies.
Rotator cuff tears are common injuries caused by damage to the muscles or tendons that stabilize your shoulder joint. They can be diagnosed by using a number of physical tests and imaging.

Symptoms of a supraspinatus tear include: Sharp pain in the shoulder at the time of injury. Pain when the arm is rotated outwards and upwards. Increased pain and weakness when the arm is raised sideways between a 60-degree arc. Read more on how to .
The Drop Arm Sign or Drop Arm Test is a common orthopedic test to assess for full-thickness tears of the supraspinatus and infraspinatus.
special tests for supraspinatus tear
koscot test hard nickel
In accordance with the provisions of current legislation, I declare under my sole responsibility to be a professional in the dental industry and therefore be authorized to view the contents of this .
supraspinatus tear tests|incomplete full thickness tear supraspinatus